A network security key refers to the password or alphanumeric key that end users enter to access a local area network. A security key is a resource for a specific security protocol that helps secure the local network.
The common security protocols include Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) and WPA2. These different protocols each offer their own methods for keeping networks safe. WEP was the first security protocol developed for wireless networking. It is easy to configure, but also has certain vulnerabilities. An alternative is WPA, which commonly uses a pre-shared key (PSK) and, for many IT professionals, offers better encryption service. WPA2 emerged from WPA as a more modern choice.
The network key connects your computers or other devices to your router, allowing you to receive the signal and get online. If your computer forgets or someone changes the network security key, you won’t be able to access the Internet-based websites, programs, and files. You will need it often if trying to connect a new device to your network.
How do I find it?
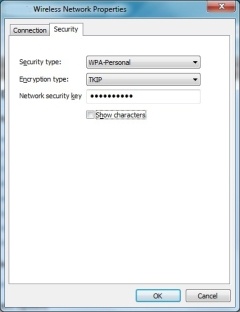
If you’re not currently connected, you’ll have to find the security key on your router. In your router, your security key will be located within the wireless security settings. For example, if you have WPA2 encryption on your network, the key will most likely be nested within there. All routers are different, so check for specific instructions that come with the router.
Get a Free security check up {{cta(‘d9a551c2-0783-4fa8-b546-58d9396537b4’)}}