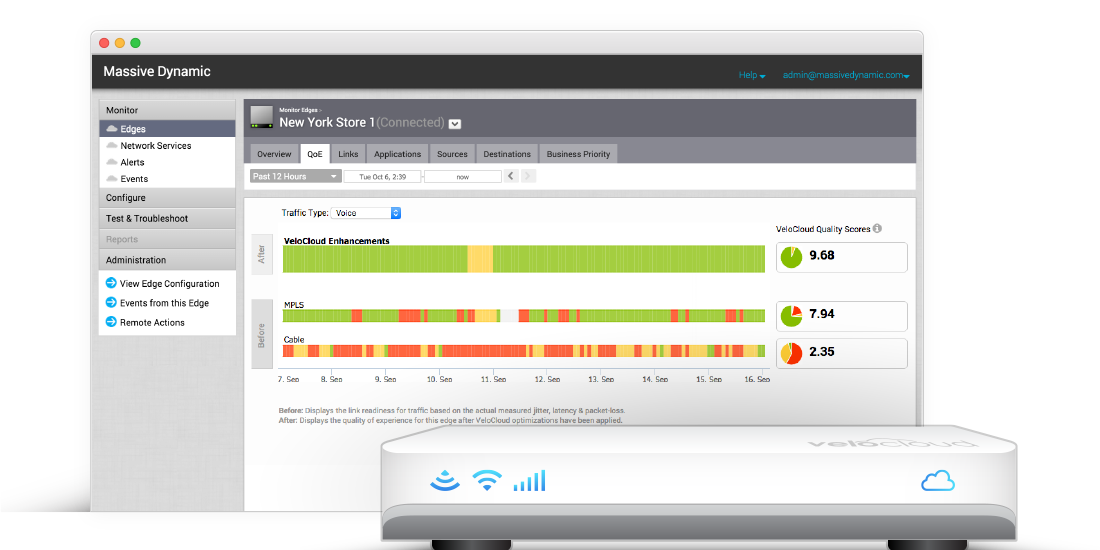
Software‐Defined WAN, or SD‐WAN for short, is at the leading edge of software‐based networking deployments. SD WAN simplifies branch networking by automating deployment and improving performance. SD WAN can be provisioned over private connectivity(MPLS), Internet connectivity and LTE links for today’s increasingly distributed networks. SD WAN offers enterprise-grade connection to cloud and enterprise applications, software defined control, and automation and virtual services delivery. Software Defined WAN uses QoE (quality of experience) to replace QoS (quality service). QoE provides end to end awareness along the entire path or multiple paths between hops and has hypersonic hitless 2ms failover, network remediation (pkt loss, jitter, oos), b/w awareness, SD WAN also offers AI (artificial intelligence) results driven, link steering and loading.
Software defined WAN can reduce IT complexity and costs with a REAL not imaginary single pane of glass. Expand globally without being stuck within a limited geographic area of connectivity. SD WAN can take broadband Internet or whatever you have available to a location and create an encrypted path back to the corporate network.
SD-WAN consists of 3 key components: An Orchestrator, Cloud Gateways and Edge Devices.
- The Orchestrator is the “brain” or management plane where everything is centrally configured, managed, updated and viewed.
- The cloud gateways are paravirtualized VMs at the service providers. These maintain
- Edge Devices
Hybrid WAN utilizes a combination of private WAN and Internet links. While enterprises do utilize dual private WAN links, increasing private WAN bandwidth can be cost prohibi-tive or slow due to the circuit availability. A properly designed SD‐WAN overcomes the challenge of managing the application performance across heterogeneous networks.SD‐WAN business policy abstraction provides full utilization of all the available links without requiring an operator to manually tune the routing protocol for every application over each link. As an example, high priority real‐time applications can traverse the more reliable private WAN links while still being able to use the Internet/broadband links for bursts. File transfer applications can utilize the aggregate bandwidth across all links. If enterprises require an application to be pinned to a specific link for compliance or security reason, SD‐WAN provides a very easy option to control the link selection on a per‐application basis.